Home Page | My Works | Seminar | BURP Thesis | Contents
CHAPTER TWO
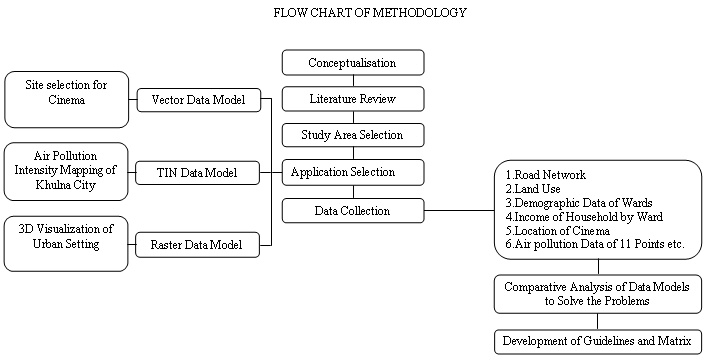
Methodology
With the development of modern technology planning functions become comparatively more easy and efficient. GIS is one of the tools, which can help planners from digital storage of data to decision making on different planning issues with automation capability. But this planning application of GIS will not produce expected result if perfect method and data model is not applied. It could influence the final result greatly. The concept of this study comes from the need of this important issue.
Under literature review the studies and the publications related to this study have reviewed.
1. NCGIA (The National Center for Geographic Information Analysis), Training Papers.
“Geographic variation in real world is infinitely complex. It would take an infinitely large database to capture the real world precisely. Data must somehow be reduced to a finite and manageable quantity by a process of generalization or abstraction”. Data model has discussed here as a requirement of this generalization or abstraction. The data models have divided into two major groups: Raster data model and Vector data model. The basic concept of the data models have described in brief here. How raster data can be created described elaborately in this manual. The application of raster data model and capabilities of raster and vector data model also described here.
2. ESRI, Inc. (1997): ARC/INFO 7.2 User Manual, Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc.
The spatial modeling section of this electronic help file has described Grid (one type of raster) and TIN (Triangulated Irregular Network) elaborately. The description contains detailed structure of data model, description of the component of the model, relative capabilities of the models and its capabilities of spatial modeling.
3. ESRI, Inc. (1996): ArcView GIS User Manual, Environmental Systems Research Institute Inc. Redlands, California.
Detailed capabilities, using process, data analysis capacity of popular GIS software ArcView GIS have described in this user manual of ArcView GIS. This software can work with raster data model, vector data model, TIN with some extension that is this program becomes the host program, which creates the environment for the extensions.
4. ESRI, Inc (1996): Avenue User Manual, Environmental Systems Research Institute Inc. Redlands, California.
User manual of an object oriented programming language under ArcView GIS. The techniques, how avenue can be used to customized ArcView to improve its capabilities of data analysis and make it more useful have described in this ESRI publication.
5. ESRI, Inc. (1996) ArcView Spatial Analyst User Manual, Environmental Systems Research Institute Inc. Redlands, California.
User manual of an extension for ArcView GIS, which add ArcView the capacity to work with raster or GRID data model. The subject matter of the publication is to express the using process of Spatial Analyst in ArcView environment and through Avenue in ArcView environment.
6. ESRI, Inc (1997): ArcView 3D Analyst User Manual, Environmental Systems Research Institute Inc. Redlands, California.
User manual of an extension for ArcView GIS, which added ArcView the capacity to work with 3D feature and TIN data model. This ESRI publication has discussed about the use of 3D Analyst under ArcView GIS and its analytical capacity through Avenue.
7. ESRI, Inc (July 1998): ESRI Shapefile Technical Description, an ESRI Write Paper. Environmental Systems Research Institute Inc. Redlands, California.
Here the technical aspects of Shapefile have described. The detailed structure of shape file to store vector data and how Shapefile link with dBase file have described here.
8. Microimage, Inc. (1997): TNTlite V5.7 User Manual
This excessive detailed user manual has described the use of the software but with this it has described many basic GIS concepts, terms and different aspects of GIS data model.
9. Geo Asia Pacific: The Geographic technology Publication for the Asia Pacific Region
A popular international journal, which publishes the modern software and hardware update, studies and applications of GIS and Remote Sensing. The articles of this journal describe the modern use of the GIS in different applied field. Articles related with this study are:
A. Nicolson, Kym. (1998): Planning for People: Integrating Social GIS Data in Urban Planning, Geographical Analysis and Research Unit, South Australian Department for Transport, Urban Planning and the Art, Adelaide, South Australia. Published in GIS Asia Pacific August/September 1998.
“Urban planning programs have traditionally overlooked the social impacts of development plans, choosing instead of concentrate on the physical and economic aspects of planning. One reason why social impacts have not received the same attention is the lack of socio-economic data relative to that which is available for the physical environment. This imbalance is particularly evident in GIS applications, where there is usually a predominance of environmental, topographic and infrastructure data.
South Australian Department for Transport, Urban Planning and the Art (DTUPA) is attempting to address this imbalance and promote the greater use of socio-economic data, through the development of a GIS based, integrated planning database called The Socio-economic Database of South Australia (SEDB). This database includes a wide variety of information on both the population and urban environment of South Australia and, in particular, for the state’s capital city, Adelaide.”
Here they have successfully used vector data model to store information on
Services and Facilities
- Education
- Health
- Child care
- Emergency service
- Churches
- Recreation
- Public transport
Land Use
- Current land use
- Open space
- Industrial locations
- Retail locations
Population
- Demographic characteristics
- Population projections
Land and Housing
- Number of dwellings
- Age and type of dwellings
- Available allotment
- Broad area land
- Forecast allotment demand
B. Agrawal, Bithi. (1998): Bangalore’s Urban GIS, Technology Informatics Design Endeavour (TIDE). Published in GIS Asia Pacific August/September 1998.
The benefits of using GIS instead of traditional paper map to store data and how GIS can be a good planning tool for the urban management have described here. They mainly used vector data model to store spatial data for urban management.
C. Iftekhar, G. Chowdhury and Zia M. Haider (1999): Creating a road Inventory with GPS, CARE Bangladesh. Published in Geo Asia Pacific August/September 1999.
Here the preparation process of Road Inventory Map of Bangladesh by Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) have described using vector data model with information like District head quarter, Thana head quarter, Union head quarter, Growth center, Hat/Bazaar, Link road, River ghat, Railway, Culvert/Bridge types, Road With Surface type and structure condition.
10. International Institute for Aerospace Survey and Earth Science (ITC).
ITC Journal publishes international studies on GIS and Remote Sensing. The journal also publishes the title of PhD and Master Degree thesis and book news of GIS and Remote Sensing. Some articles about Digital Elevation Model (DEM) and TIN are helpful to understand the practical use of different data models. The articles related with this study are
A. Klaus Tempfli, (1998): 3D Topographic Mapping for Urban GIS. Published in ITC Journal 1998-3/4.
The paper has reviewed requirements for an urban GIS and analyses topographic objects, the most important class of urban objects. It has explained adopted data model and the derived polygonal data structure. The structure support full 3D geometry and topology and incorporates raster data for photo-texture.
B. José A Martínez-Casasnovas and H John Stuiver, (1998): Automated Delineation of Drainage Networks and Elementary Catchments from Digital Elevation Models, Department of Environment and Soil Science, University of Lleida, Rovira Roure 177, 25198 Lleida, Spain and Department of Geographic Information Processing and Remote Sensing, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands. Published in ITC Journal 1998-3/4.
This paper has shown a successful application process of Digital Elevation Model (DEM), reclassification of raster data and rasterisation and vectorisation of Grid data.
11. Kiyingi, K.G. (1998): Integration of Digital Elevation Models and GIS: a potential for planning and design of sewer systems in Dar es Salaam.
Here the characteristics, structure, methods of DEM creation with advantages and disadvantages of the methods and accuracy of DEM have described. In this thesis a successful application of DEM to delineate sewerage systems for Dar es Salam, Tanzania have shown.
12. Aronoff, Stan. 1993, Geographic Information System: A management Perspective.
Basic concepts of GIS have described here clearly. Data models also have divided in two groups DBMS and Spatial data model. The spatial data model and DBMS have described with its individual characteristic.
13. P. A. Burrough, 1985, Principal of Geographic Information System for Land Resource Assessment.
Data structures for thematic maps, database structure, raster and vector data structure have discussed with different technical aspects. Definition, use, product, importance and methods of representing Digital Elevation Model (DEM) have also discussed in this book.
The studies mentioned above have some relation with this study but no study has incorporating three data models at a time. No one has judged the data models before using it in the practical applications. They have not considered that data model can influence the result.
The researchers of the above mentioned studies were from different fields. Many of them are not from planning field. So they take the problems at their point of view not always at the standpoint of a planner. This study will produce some guidelines for the planner, which will help them to select perfect data model that suite their purpose.
Khulna City is located on the banks of the river Rupsha and Bhairab. Khulna is bounded by Bhairab River and Fultala Thana on the north, by the Rupsha River on the east, by the Rupsha River on the south and on the west by Dumuria Thana.
Like other cities of Bangladesh Khulna City has grown naturally in an unplanned manner. No large planning activities occur in Khulna before 1961, when the first master plan of Khulna was prepared. Although the master plan was not implemented properly. After that no master plan for Khulna City has prepared till 2001. Although a master plan preparation project is on going. In this condition the city is growing in an uncontrolled manner. To ensure sound access to urban basic services and livable physical environment it is urgent to guide the development of the city with modern technology. GIS can be the useful tool, which can help planners to prepare plan accurately in short time as it have automation capabilities.
In fact there are many scopes for GIS based planning applications in Khulna City. It is not possible to accommodate all the applications in a study. So three applications have been selected for this study where one application can be conducted using one data model.
Vector Data Model Application
Site selection for cinema in Khulna City as a recreational facility for low income people
In Khulna City there is a lack of urban services and facilities. Like other urban facilities recreational facilities of the city is not adequate. There is a shortage of playgrounds, community centers, theaters and cinemas etc. Cinema can be a media of recreation to the people. But access to cinema is not adequate from every place of Khulna City. So the first application of this study is to find out the suitable location for cinema where it is necessary and which could be applied to locate other recreational facilities.
The existing accessibility of cinema has been analysed using PC ARC/INFO Network. The unserved has been found out using Network Allocation. The optimum location for cinema has been analysed using buffer and overlay techniques.
Working Process
A. Editing the input coverages
The coverages, which were used in this application, have been edited to make it usable for the application.
B. Data entry
The capacity of each cinema has been stored as an attribute of the point coverage. The demand item has been calculated from field survey and the demographic data of each ward. The total demand of a ward has been divided to the road arc of that ward. Then using PC ARC/INFO ALLOCATE the allocated and unallocated arc has been found out.
C. Creating allocated polygon
The allocated polygons have been created adding the end of the allocated arc.
D. Unallocated polygon
The allocated polygons have been overlayed on ward coverage of KHULNA CITY to find out the unallocated area.
E. Suitable location
Suitable locations have been found out based on some logical criteria using buffer and overlay technique.
Raster Data Model Application
Air pollution intensity mapping of Khulna City as health risk to urbanites
The continuous degradation of environment and its increasing hazards to public health make people more conscious about the environment. Environmental pollution is a major threat to the existence of human and other living being. It has to be controlled for the benefit of the existence of human being. To control the pollution at first it is necessary to know the intensity of pollution at a place and tolerable limit.
This application will use the intensity of air pollutants at some points of Khulna City. The intensity value will be interpolated to get a DEM of pollutant Intensity at other places of Khulna City, which will be a guideline for the planner and decision maker to select place where to take immediate action.
Working process
A. Digitizing
The points have been digitized in Khulna City ward coverage
B. Editing the input coverages
The input coverages have been be edited to make it usable for this application.
C. Data entry
The air pollution data have to be stored as attribute of a point coverage for interpolation. Concentration of Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM), SOx and NOx, will be stored at Point Attribute Table of the points.
D. Interpolation
The points have been interpolated for each of the pollutant individually using IDW method. Thus 3 Grid themes of different pollutants have been produce.
E. Weighted Overlay
Comparative pollutant intensity map has been created from weighted overlay of the 3 pollutants themes using Model Builder (a component of Spatial Analyst 2 of ArcView)
TIN Data Model Application
3D visualization of urban setting based on TIN data model with Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) and Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML).
3D GIS have great potentiality in urban planning. 3D GIS can be used for guiding city development, urban landscape architecture, conservation, site selection, conflict resolution in urban planning, environmental analysis, simulation of any large scale development, planning and management of public utilities, tourism and entertainment. 3D visualization is one of the most important parts of 3D GIS to analysis and visualize 3D data.
This application will prepare a surface TIN and the other infrastructure on the surface and display it in a 3D view. This application will also discuss the use of the 3D view of the urban setting.
Working process
A. Digitizing
The topographic maps of the selected areas have been digitized using PC ARC/INFO.
a. The spot heights have been stored as attribute of a point coverage
b. The height of buildings have been stored as an attribute of a polygon coverage
c. The height of roads have been stored as an attribute of a polygon coverage
B. Interpolation
The point coverages have been interpolated to create a surface DEM using ArcView Spatial Analyst 2. Interpolation method was IDW.
C. Creating TIN
The surface DEMs have been converted to TIN. The buildings and roads coverages have been given comparative height taking the surface DEM as base height.
D. 3D Visualization
The produced TINs have been edited to make a 3D visualization and exported to VRML 2 format. The VRML files have been edited and a web page has been designed to present 3D Visualization model of urban setting.
The on going master plan project for Khulna City have collected many data of Khulna City which is necessary for this study. The main data source of this study is the survey data of Khulna master plan project and Environmental maps and workbook for Khulna City, Bangladesh, project sponsored by USAID and prepared by Urban and Rural Planning Discipline of Khulna University.
The available useable data are
1. Road Network
2. Land Use
3. Demographic Data of Wards
4. Income of Household by Ward
5. Location of Cinema and Other Facilities
6. Air Pollution Data
7. Topographic Map
8. Spot height, Building Height.
2.6 Comparative Analysis of Data Models
From the analysis of the data models and the application of the data models comparative advantages and disadvantages of the data models in different cases have been found out. This study also gives guidelines of choosing a particular data model for a planning application considering reasonable efficiency of the result. That is which data model is perfect for what purpose
2.7 Development of Guidelines and Matrix
A matrix for selecting data model in planning applications have been developed analysing the results of the studies.